In China's major chemical accident prevention system, the current " two key and one major " regulatory system is adopted. Improve the intrinsic safety level by grasping “ key hazardous chemical processes â€; control the total number of hazardous chemical accidents by focusing on “ mainly monitoring hazardous chemicals â€; and arresting large hazardous chemical accidents by grasping “ significant hazard sources â€.
  Â
First, the definition
    Major hazard is a concept that has been proposed in related studies to prevent and control major accidents of hazardous chemicals.
    In general, the definition of major hazard sources is mainly divided into two categories, one is determined by functional units , such as the major hazard installation in the Seveso Act issued by the European Community. This concept is also used in the International Labour Organization's Convention on the Prevention of Major Industrial Accidents (No. 174); the United States mainly adopts the concept of process safety; the other uses major sources of danger according to the entire enterprise area . determine.
    Our country's definition of major hazard sources is mainly based on the Seveso Act, defined as: units that produce, process, use or store hazardous chemicals on a long-term or temporary basis, and the number of hazardous chemicals equals or exceeds a critical amount .
Second, management basis
    When a company has a major source of danger, in addition to the need to conduct safety product safety supervision registration, it also needs a series of work such as staff training, hazard source monitoring, and emergency planning. The management basis of major hazard sources are mainly as follows, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Management basis and content of major hazard sources

    At the same time, China's safety supervision and management of major hazards is based on the principle of combining local supervision with hierarchical management . The safety production supervision and administration department of the local people's government at or above the county level shall implement safety supervision and management of major hazards in its jurisdiction in accordance with the relevant laws, regulations and standards as stated in the above table.
Third, identification and evaluation
    Identification and evaluation are the top priority in the management of major hazard sources. The accuracy of this link directly affects the subsequent safety management. Therefore, any company and organization should be treated with caution. The main process is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Identification and evaluation process
1) Identification
    The current identification of major hazard sources in China is based on GB18218-2009 (click to download), which identifies hazard sources based on the hazard characteristics of hazardous chemicals and their quantities and the critical mass of hazardous chemicals.
    Two important tables are given in GB18218-2009 to identify if the unit in which the chemical is located is a significant source of hazard. One of the tables (shown in Table 2) lists the specific 78 chemical lists and their critical masses, and the other table (shown in Table 3) lists all hazard categories covered by major hazards and their Corresponding critical mass.
Table 2 Names of hazardous chemicals and their critical masses (example)
| Serial number | category | Hazardous Chemicals Name and Description | Critical amount (T) |
| 1 | Explosives | Barium azide | 0.5 |
| 2 | Lead azide | 0.5 | |
| 8 | Ammonium nitrate (including combustibles >0.2%) | 10 | |
| Click to view or download the full version of the form | |||
Table 3 Non-listed hazardous chemicals categories and their critical masses (example)
| category | Hazard classification and description | Critical amount |
| Flammable solid | Substances whose hazard is 4.1 and packaged as Class I | 200 |
| Oxidizing substance | Substances whose hazard is 5.1 and packaged as Class I | 50 |
| Substances whose hazard is 5.1 and packaged as Class II or Class III | 200 | |
| Click to view or download the full version of the form | ||
    When there are many dangerous chemicals in the unit, it needs to be calculated according to formula (1) before judging whether it is a major hazard.
Q1/Q1+q2/Q2+· ·····+qn/QN≥1 ( 1 )
In the formula:
Q1, q2, ... qn - the actual amount of each hazardous chemical, in tons (t);
Q1, Q2...QN - the critical amount corresponding to each hazardous chemical, in tons (t).
At the same time, major hazards are subject to the following four principles in the identification process:

2) Classification
    In China, the major hazard sources are divided into 4 levels according to the degree of risk, and the level depends on the R value.
Table 4 Corresponding relationship between major hazard source levels and R values ​​of hazardous chemicals
| Major hazard source level of hazardous chemicals | R value |
| First level | R≥100 |
| Secondary | 100>R≥50 |
| Third level | 50>R≥10 |
| Level four | R<10 |
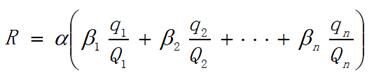 (2)
(2) In formula (2):
The meaning of q and Q is shown in formula (1);
α—The correction factor for exposed personnel outside the factory depends on the number of permanent residents within 500 meters of the boundary of the major hazardous source plant. The value of α is proportional to the number of people, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5 Calibration coefficient α value table
| Number of people exposed outside the factory | α value |
| More than 100 people | 2.0 |
| 50 to 99 people | 1.5 |
| 30 to 49 people | 1.2 |
| 1~29 people | 1.0 |
| 0 people | 0.5 |
Table 6 Correction coefficient β value table
| Hazardous chemicals category | Toxic gas | Explosives | Flammable gas | Other dangerous chemicals |
| 值 value | See Table 7 | 2 | 1.5 | 1 |
Table 7 Common Toxic Gas Correction Coefficient β Value Table
| Toxic gas name | Carbon monoxide | Sulfur dioxide | ammonia | Ethylene oxide | Hydrogen chloride | Methyl bromide | chlorine |
| 值 value | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Toxic gas name | Hydrogen sulfide | Hydrogen fluoride | Hydrogen cyanide | Nitrogen dioxide | Carbonyl chloride | Phosphine | Methyl isocyanate |
| 值 value | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Note: The toxic gases not listed in Table 7 can be taken as β=2, and the highly toxic gases can be taken as β=4. | |||||||
3) Safety assessment
    Article 38 of the "Safe Production Law" states that: the hazardous chemical production and business units need to conduct regular assessments of major hazards. Therefore, from a legal perspective, safety assessment is one of the legal obligations of hazardous chemicals companies . Under actual circumstances, the enterprise may evaluate it by itself or entrust a safety evaluation agency.
However, for primary or secondary major hazard sources of toxic gases, explosives, and liquefied flammable gases, safety assessment agencies must be entrusted to perform a quantitative risk assessment ( QRA ) approach.
    The contents of the safety assessment mainly include the following points, as shown in Table 8.
Table 8 Main contents of the safety assessment

4) Need to be re-identified, graded, and evaluated <br> In the above, we explained the three important aspects of identification, grading and evaluation. However, in the following cases, the above behavior needs to be repeated. As shown below.

Self drilling Screw made of 410 stainless steel, high hardness (40 Rockwell C), steel process.
Drilling screw is also very strong hardness, compared to the ordinary screw up, not only to maintain the ability is good, the connection object effect is also very strong, for the performance of the screw, are generally does not need auxiliary processing, can be directly on the object directly drill a Kong Sue into objects, not just use rise very convenient, Also can greatly improve the efficiency of work. This kind of drilling screw can be said to be the first choice of workers in various fields.
So what is the use of drilling screws?
1 stainless steel plate, metal plate, galvanized steel plate, engineering installation.
2 metal curtain wall metal light compartment and other indoor and outdoor installation.
General Angle steel, channel steel, iron plate and other metal materials combined installation.
4, automobile, container, shipbuilding, refrigeration equipment and other assembly projects.
Self drilling screw,hex Self drilling screw,truss Self drilling screw,flat Self drilling screw,pan Self drilling screw
Shenzhen Lanejoy Technology Co.,LTD , https://www.injectionnut.com