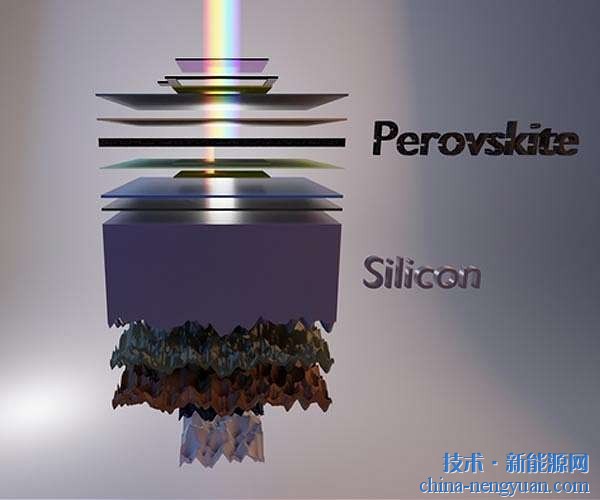
 |
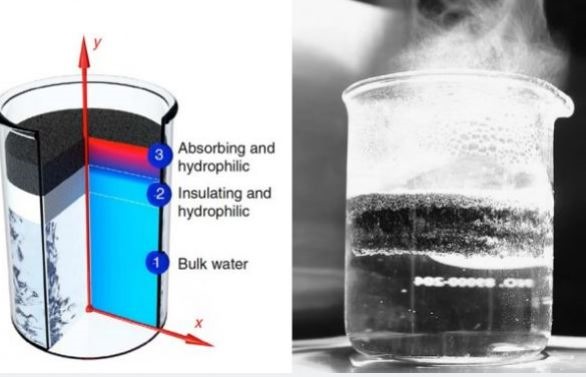
Graphene is indeed a star material for the future. We have seen its active presence in many fields. Nowadays, MIT announced that it has found a new method for extracting clean drinking water. The protagonist is still it. In regions where water is scarce, evaporating seawater is a viable option, which requires the use of specialized solar evaporators. However, the obvious drawback of this method is that the output is too low, and solar evaporators need to consume a lot of energy, which is unacceptable for backward areas.
The scientists first heated the graphene with microwaves for exactly 7 seconds, making it a low-density porous structure that floats on the salt water surface. After this, graphene absorbs the energy from the sun and passes it directly to the brine, which is very efficient in evaporation.
This technology is not yet mature enough to be applied on a large scale. Scientists say that its most obvious drawback is that some parts of salt after evaporation easily block the pores of graphene, resulting in decreased efficiency over time. Researchers are trying to solve this problem.
Ningbo Wason Lighting Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.wasonlights.com