Zinc batteries are a type of energy storage system that uses zinc metal or zinc oxide as the negative electrode active material, and has an indelible position in the battery development process. Zinc has the advantages of abundant resources, high safety, low cost and multi-electron transfer mechanism, which makes its volume specific capacity much higher than lithium. Although the development of zinc batteries has encountered stagnation in the past 20 years, with the increasing awareness of green and environmental protection in recent years and the development trend of lead-free, zinc batteries have ushered in a new round of worldwide attention. It has great application prospects in the fields of vehicles, large-scale energy storage and special fields. However, the short cycle life is still the biggest obstacle to its application today, which is why the current application of zinc batteries is still based on primary batteries. Therefore, focusing on the key scientific issues of zinc storage chemistry and effectively improving the recharging efficiency is the key to the secondary zinc battery once again on the stage of history.
Relying on the Qingdao Energy Storage Industry Technology Research Institute ("Qingdao Energy Storage Institute") constructed by the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Process Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, from the perspective of zinc battery core electrolyte development and interface design, in terms of long-life, high-stability zinc secondary batteries Obtained important research results. In 2016, Qingdao Energy Storage Institute realized the new system of 2.35 V high voltage zinc secondary battery for the first time using ultra-high concentration salt-in-water electrolyte (Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 6, 69). In 2017, Qingdao Energy Storage Institute innovatively solved the problem of zinc anode-electrolyte interface wettability with a low-temperature repair strategy, providing strong technical support for the application of zinc batteries in harsh conditions such as aerospace and deep-sea low temperature ( Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7871; authorized patent. 3).
Since 2018, Qingdao Energy Storage Institute has developed a series of eutectic zinc-based electrolyte systems with highly adjustable solvation structure, physicochemical properties, and ion transport behavior (Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5374; Nano Energy 2019, 57, 625; Electrochim. Acta 2018, 280, 108; authorized patent. 2). Importantly, the in-situ solid electrolyte layer (SEI) was successfully constructed on the surface of the zinc anode for the first time, deepening the traditional cognition of the multi-metal interface ion interface transport layer. Inspired by the "brightener" in the electroplating industry, Qingdao Energy Storage Institute further proposed a modification strategy for amide polymers. In the traditional aqueous electrolyte, the zinc anode was precisely regulated from the aspects of side reaction inhibition and uniform deposition, and the cycle life exceeded 8000 h. (Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1938; patent. 0). Based on the previous research progress, the team deeply analyzed the key problems, especially in terms of poor reversibility of the negative electrode and failure mechanism, and made a useful strategy for the design of the liquid / polymer electrolyte structure. Application development provides a constructive solution (NPG Asia Mater. 2019, DOI: 10.1038 / s41427-019-0167-1).
The above research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R & D Program, the Two Integration Funds, and the Youth Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
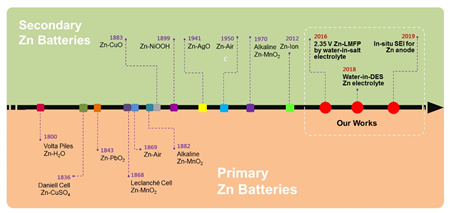
The historical evolution of zinc battery system and the research progress of Qingdao Energy Storage Institute
Disposable Coverall Gown,Hospital Isolation Gowns,Isolation Gown Coverall,Disposable Isolation Gowns
Ningbo Autrends Prevention Products Co., Ltd , https://www.autrendsafety.com