1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
There are large differences in the application rates of organic fertilizers in different fields in the production of sweet potato, the phenomenon of blind application of nitrogen fertilizer is serious, the application of potassium fertilizer is insufficient, the phenomenon of “heavy mass elements, light and medium elements†is common, the application period and mode are unreasonable, and excessive irrigation To cause problems such as water and fertilizer waste, the following fertilization principles are proposed:
(1) Rational application of organic fertilizer, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer application, the application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer should follow the principles of nitrogen control, phosphorus stabilization and potassium increase;
(2) The distribution of fertilizers is mainly based on base and chasing; the topdressing is mainly based on nitrogen fertilizer, and the potassium fertilizer is rationally combined;
(3) Pay attention to proper application of trace elements such as calcium and boron during the rosette period to the end of the ball to prevent the occurrence of diseases such as “dry heartburnâ€;
(4) When the acidification of vegetables is serious, an appropriate amount of acidic soil conditioner such as lime should be applied;
(5) Combine with high-yield cultivation techniques, especially water-saving irrigation technology, to give full play to the coupling effect of water and fertilizer and improve fertilizer utilization.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) Applying high-quality farmyard manure 2 square meters per mu.
(2) The production level is above 6500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 18~20 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 8~10 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 14~16 kg/mu.
(3) The production level is 5500~6500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 15~18 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 6~8 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 12~14 kg/mu.
(4) The production level is 4500~5500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 13~15 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 4~6 kg/mu, potassium fertilizer (K2O) 8~10 kg/mu.
For the more serious plots of “dry heartburn†in previous years, pay attention to nitrogen and calcium supplementation, and spray 0.3%~0.5% calcium chloride (CaCl2) solution 2~3 times from the rosette stage to the late stage of the ball formation; When the soil pH of the vegetable garden is less than 5, 100-150 kg of quicklime is applied per acre; when the soil pH is <4.5, 150-200 kg of quicklime is applied per acre. For the boron-deficient plots, 0.5~1 kg/mu of borax may be applied, or 0.2%~0.3% of borax solution may be sprayed 2~3 times. At the same time, it can be sprayed with spraying 2~3 times of 0.5% potassium dihydrogen phosphate to increase the vegetable yield and commodity rate of cabbage.
Nitrogen and potassium fertilizer 30%~40% base application, 60%~70% in the rosette stage and the initial stage of ball formation, and the phosphate fertilizer is used as the base fertilizer or hole application.
radish
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
In view of the diazo phosphate fertilizer light potassium fertilizer existing in radish production, the proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is imbalanced, the application period of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer is unreasonable, the application of organic fertilizer is obviously insufficient, and the importance of trace element application is insufficient. The following fertilization principles are proposed:
(1) According to the soil fertility conditions and target yield, optimize the dosage of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, pay special attention to adjusting the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers and increase the application of potassium fertilizer;
(2) The content of trace elements such as manganese, zinc, boron and molybdenum in the northern calcareous soil is low, and the supplement of trace elements should be paid attention to; when the acidification of vegetables in the south is serious, the acid soil conditioner such as lime should be applied in an appropriate amount;
(3) Reasonable application of organic fertilizers significantly increases radish yield and quality, avoids the use of organic fertilizers that are not fully decomposed, and promotes the application of commercial organic fertilizers and decomposed farmyard manure.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) Application rate of organic fertilizer: small radish (such as four season radish) with a production level of 1000~1500 kg/mu can be applied 0.5~1 square/mu of organic fertilizer; high yield of organic product with yield level of 4500~5000 kg/mu Fertilizer 2~3 squares/mu.
(2) The production level is above 4000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 15~18 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 5~7 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 12~14 kg/mu.
(3) The production level is 2500~3000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 10~13 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 4~6 kg/mu, potassium fertilizer (K2O) 10~12 kg/mu.
(4) The production level is 1000~1500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 6~9 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 3~5 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 8~10 kg/mu.
If the base fertilizer is not applied with organic fertilizer, increase nitrogen fertilizer (N) 3~5 kg/mu and potash fertilizer (K2O) 2~3 kg/mu as appropriate.
For plots that are prone to the lack of trace elements of boron, or those that have been shown to have boron deficiency symptoms in previous years, 1 kg of borax per acre may be applied before sowing, or 0.1% to 0.5% of borax may be used in the middle and late stages of radish growth. The boric acid aqueous solution is sprayed on the foliar surface (may also be sprayed with pesticides), sprayed once every 5 to 6 days, and sprayed 2 to 3 times.
All organic fertilizers were applied as base fertilizer. 40% of the total nitrogen fertilizer was used as base fertilizer, 60% in the rosette stage and the fleshy root was pre-growed twice for topdressing application; the phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were all applied as base fertilizer, or 2/3 potash as base fertilizer, 1 /3 is applied in the early stage of fleshy root growth.
Chinese cabbage
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
In view of the serious problem of blind application of nitrogen fertilizer in the production of Chinese cabbage, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer is too large, the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is unreasonable, the application of high-phosphorus compound fertilizer is blindly applied, the application of organic fertilizer in some areas is insufficient, and the acidification of vegetable soil is serious. , propose the following fertilization principles:
(1) Optimize the amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer according to soil fertility conditions and target yield;
(2) Based on base fertilizer, combined with base fertilizer and topdressing. The topdressing is mainly based on nitrogen fertilizer, and the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are reasonably matched, and the trace elements are appropriately supplemented. After the rosette period, strengthen the management of topdressing, and increase the topdressing in the early stage of the package. It is not suitable to trace the nitrogen fertilizer 2 weeks before harvesting;
(3) The content of trace elements such as boron and molybdenum in the calcareous soil in the north is low, and attention should be paid to the supplement of trace elements;
(4) When the acidification of vegetables is serious, an appropriate amount of acidic soil conditioner such as lime should be applied;
(5) Avoid using organic fertilizer that is not fully decomposed, and advocate the application of commercial organic fertilizer and fertile farmyard manure to fertilize soil.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) Application rate of organic fertilizer: the production level is 4500~6000 kg/mu, the organic fertilizer is 2~3 square/mu; the production level is 3500~5000 kg/mu, and the organic fertilizer is 2 square/mu.
(2) The production level is 4500~6000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 18~23 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 5~8 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 16~20 kg/mu.
(3) The production level is 3500~4500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 15~20 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 4~6 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 13~17 kg/mu.
If the base fertilizer is not applied with organic fertilizer, increase nitrogen fertilizer (N) 3~5 kg/mu and potash fertilizer (K2O) 2~3 kg/mu as appropriate.
For plots that are prone to the lack of boron trace elements, or for plots that have been characterized by boron deficiency in previous years, 1 kg of borax per acre may be applied before sowing, or 0.1% to 0.5% of borax or boric acid in the middle and late growth stages. The aqueous solution is sprayed on the foliar surface (may also be mixed with pesticides), sprayed once every 5~6 days, and sprayed 2~3 times; when the soil pH of the southern vegetable field is <5, 100-150 kg of quicklime is applied per acre. It can reduce soil acidity and supplement calcium.
All organic fertilizers and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers were applied as base fertilizers, 30% of nitrogen fertilizers were used as base fertilizers, and 70% were applied as top dressings in combination with irrigation in the rosette stage and pre-cardiac stage.
lettuce
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
In view of the problem that the application amount of organic fertilizer in lettuce production is small, the phenomenon of blind application of nitrogen fertilizer is prominent, the application amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer is insufficient, and the fertilization period and method are unreasonable, the following fertilization principles are proposed:
(1) Adding organic fertilizer, controlling nitrogen fertilizer, and increasing phosphorus and potassium fertilizer; (2) The fertilizer distribution method is based on base and chasing. Topdressing is mainly based on nitrogen fertilizer, and rational application of potassium fertilizer;
(3) For acidified vegetable gardens, acid soil conditioners such as lime should be applied in an appropriate amount;
(4) Fertilization combined with high-quality cultivation techniques, especially water management, to improve the efficiency of fertilizer and water use.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) The base fertilizer is applied once 1000-1500 kg/mu of decomposed farmyard manure.
(2) The production level is above 3500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 16~18 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 7~9 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 8~10 kg/mu.
(3) The production level is 2500~3000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 14~16 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 5~6 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 6~8 kg/mu.
(4) The production level is 1500~2000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 12~14 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 4~5 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 5~6 kg/mu.
The acid resistance of lettuce is very poor. When the soil pH of the vegetable garden in the south is less than 5, 150 to 200 kg of quicklime is applied per acre.
Nitrogen fertilizers are all topdressed, according to 20%, 30% and 50% in the transplanting and returning period, the rosette stage and the early stage of rapid growth, the application of the potassium fertilizer is 40%~50%, and the rest is in the rosette stage and the early stage of rapid growth. After two times of application, the phosphate fertilizer is used as the base fertilizer or acupoint application.
Facility tomato
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
Most of the northern regions such as North China are solar greenhouses, and most of them are small and medium-sized arch sheds in central and southwestern China. There are excessive fertilization in production, the use of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers is high, the proportion of nutrient input is unreasonable, and the accumulation of soil nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients is obvious. Excessive irrigation leads to serious nutrient loss, soil acidification is common, soil calcium, magnesium, boron and other elements supply obstacles, continuous cropping obstacles lead to serious soil quality degradation, nutrient absorption efficiency and vegetable quality decline, etc., the following fertilization principles are proposed:
(1) Rational application of organic fertilizer, adjustment of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers; non-calcium soil and acid soils need to be supplemented with trace elements such as calcium, magnesium and boron;
(2) According to crop yield, sorghum and soil fertility conditions, rational allocation of chemical fertilizers, most of the phosphorus fertilizer application, nitrogen and potassium fertilizers; early spring growth should not be frequently topdressed, pay attention to post-flowering and late-stage topdressing;
(3) Combine with high-yield cultivation techniques, promote rooting during seedling stage, and adopt the principle of “small number of times†to rationally fertilize fertilization;
(4) The old shed with soil degradation needs to return the straw to the field or apply the organic fertilizer with high C/N ratio, reduce the application of poultry manure, increase the number of rotations, and achieve the purpose of removing salt and reducing the obstacles of continuous cropping;
(5) When the vegetable acidification is serious, an acidic soil conditioner such as lime should be applied in an appropriate amount.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) The seedling fertilizer is added to the decomposed organic fertilizer and the phosphate fertilizer is applied. For every 10 square meters of seedbed, apply 60~100 kg of decomposed poultry manure, 0.5~1 kg of calcium, magnesium and phosphate fertilizer, 0.5 kg of potassium sulfate, and spray 0.05%~0.1% urea solution 1~2 times according to the seedling condition.
(2) Applying high-quality organic fertilizer to the base fertilizer for 2~3 square meters/mu.
(3) The production level is 8000~10000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 30~40 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 15~20 kg/mu, potassium fertilizer (K2O) 40~50 kg/mu.
(4) The production level is 6000~8000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 20~30 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 10~15 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 30~35 kg/mu.
(5) The production level is 4000~6000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 15~20 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 8~10 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 20~25 kg/mu.
When the soil pH of the vegetable field is less than 6, the calcium, magnesium and boron are easily deficient. The base can be applied with lime (calcium fertilizer) 50~75 kg/mu, magnesium sulfate (magnesium fertilizer) 4~6 kg/mu, and the root is applied 2~ 3 times 0.1% boron fertilizer.
More than 70% of the phosphate fertilizer is used as the base fertilizer (point), and the rest is applied with the compound fertilizer, 20%~30% of the nitrogen and potassium fertilizer base, 70%~80% after the flowering to the ear expansion period, 3~10 times with the water. Shi, each time the application of nitrogen fertilizer (N) does not exceed 5 kg / mu.
Facility cucumber
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
The planting season of cucumber is divided into autumn and winter sorghum, wintering sorghum and winter sorghum. The blind fertilization in the production is unreasonable. The excessive fertilization leads to serious nutrient loss. The organic fertilizer applied in the vegetable field is mostly livestock. The following fertilization principles are proposed: the main fertilization principle is caused by the decrease of soil biological activity, the continuous deterioration of soil quality, the decrease of nutrient absorption efficiency and the decline of vegetable quality.
(1) Adding organic fertilizer, advocating the application of high-quality organic compost, paying attention to the application of compost with more straw, less application of poultry manure, implementation of organic and inorganic fertilizer and straw returning;
(2) According to the soil fertility conditions and the application amount of organic fertilizer, comprehensively consider the supply of environmental nutrients, and appropriately adjust the dosage of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers;
(3) Adopt reasonable irrigation techniques and follow a small number of irrigation fertilization principles;
(4) After planting, the seedling stage should not be frequently topdressed, nitrogen fertilizer and potassium fertilizer should be applied in stages, a small number of times, avoiding the application of compound fertilizer with high phosphorus content, paying attention to top and late topdressing;
(5) When the vegetable acidification is serious, an acidic soil conditioner such as lime should be applied in an appropriate amount.
2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) Incubating seedlings to increase the application of decomposed organic fertilizer, supplementing the application of phosphate fertilizer, applying 60~100 kg of decomposed organic fertilizer per 10 m2 seedbed, 0.5~1 kg of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 0.5 kg of potassium sulfate, and spraying 0.05% according to the seedling condition. 0.1% urea solution 1~2 times.
(2) Applying high-quality organic fertilizer to the base fertilizer for 3~4 square meters/mu.
(3) The production level is 14000~16000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 45~50 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 20~25 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 40~45 kg/mu.
(4) Production level 11000~14000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 37~45 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 17~20 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 35~40 kg/mu.
(5) The production level is 7000~11000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 30~37 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 12~16 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 30~35 kg/mu.
(6) The production level is 4000~7000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 20~28 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 8~11 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 25~30 kg/mu.
If drip fertigation is used, 20% of fertilizer can be reduced; if flooding is used, it is necessary to increase the amount of fertilizer by 10% to 20% per fertilization.
The whole organic fertilizer and phosphate fertilizer of cucumber are applied as base fertilizer, and the initial flowering period is mainly controlled. The total nitrogen and potassium fertilizers are regularly applied in 6~11 times according to the nutrient demand during the growing period. The amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied per time does not exceed 5 kg/mu; the nitrogen and potassium fertilizers in autumn and winter and winter and spring are divided into 6~7 times and the winter is long. The nitrogen and potassium fertilizers of the earthworms are divided into 10 to 11 times.
Southern autumn winter potato
1. Fertilization problems and fertilization principles
In view of the problems of insufficient application of organic fertilizer and potassium fertilizer in potato production in autumn and winter in the south, the following fertilization principles are proposed:
(1) Optimize the amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer according to soil fertility conditions; (2) Add organic fertilizer, promote organic-inorganic application and straw returning; (3) Appropriately increase potassium fertilizer according to soil potassium status;
(4) Fertilizer application should be combined with high-yield and high-quality cultivation techniques. 2. Fertilization amount and method
(1) The output level is 3000 kg/mu or more: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 11~13 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 5~6 kg/mu, and potassium fertilizer (K2O) 14~17 kg/mu.
(2) The production level is 2000~3000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 9~11 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 4~5 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 12~14 kg/mu.
(3) The production level is 1500~2000 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 7~9 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 3~4 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 9~12 kg/mu.
(4) The production level is below 1500 kg/mu: nitrogen fertilizer (N) 6~7 kg/mu, phosphate fertilizer (P2O5) 3~4 kg/mu, potash fertilizer (K2O) 7~8 kg/mu.
Apply 2~3 square meters of organic fertilizer per mu as base fertilizer; if organic fertilizer is applied to the base fertilizer, reduce the amount of chemical fertilizer as appropriate.
For soils deficient in boron or zinc, 1 kg/mu of borax or 1~2 kg/mu of zinc sulfate may be applied.
For areas with sulfur deficiency, sulfur can be applied at a rate of 2 kg/mu. If other sulfur-containing fertilizers are used, the amount of sulfur can be reduced.
70% of nitrogen fertilizer is used as base fertilizer, 30% is used as top dressing in seedling stage, and all phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are used as base fertilizer. Potassium fertilizers in areas with large rainfall in the growing season of the potato and soil in the soil should be applied in several stages.
Expert Group on Soil Testing and Formula Fertilization Technology of the Ministry of Agriculture
Phlizon`s COB series Grow Light emits all the wavelengths of light which can be fully absorbed by the plants to create.
Best full Specturm designed to perfectly match large areas of indooor plants, especially for Medical Plant.
COB + Dual-chip,most efficient spectrum,high PPFD.Two cooling fans with double ball(import from Japan) and big aluminum heat sink to protect the grow lights from high temperature,good cooling,long lifespan.Photosynthesis and promote healthy growth budding and flowering.
1000w/2000w /3000w COB LED Grow Light, it will give you more options when your plants need different strength of illumination.
Grow Lights are a great choice for growers who are dealing with hot HPS lights and want to change to something that's going to run cooler. Although LED Grow Lights do produce heat,the smaller models might not bring up the temperature of your grow space.Even the more powerful models of LED grow lights that produce a lot of heat still have built-in cooling systems to help prevent the heat from beaming directly down onto your plants.
1000w 2000w 3000w 400w led grow light Features
Indoor grow light
COB series, high power branded CREE COB with high Par value and deeper penetration
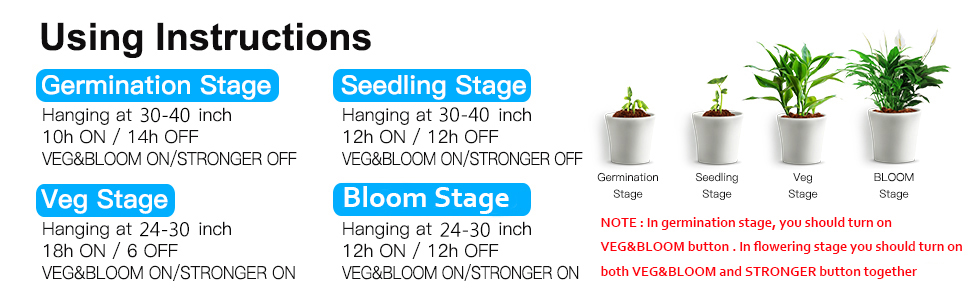
VEG/BLOOM and STRONGER switches for each grow stage.
Special spectrum for plant growing to increase the yield.
Building to Harvest: Beneficial for seeding to fruiting stage.
Good quality fans with low noise.
Easy to install by minute
Energy Saving, environmental friendly
3 Years Warranty
Compare led grow light to traditional HPS/MH grow light

WHAT MAKE UP AN EXCELLENT LED GROW LIGHT ?
1.PPFD Value : PPFD is Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density. When you choose a plant light, you should compare the PPFD values of different plant lights. The larger the value, the better the growth of the plant.
2.Actual Power: Because the actual power of the plant light always varies with different conditions, all Amazon sellers use the rated power to describe the power of the product because the rated power is constant. When you pick a LED grow light, the rated power of the plant light is a reference, and more importantly is the actual power.
3.Core Coverage: In addition to the above two, when you choose a plant light, you also need to compare the cover area of different plant lights, of course, the size of the core coverage area. In general, in germination stage, you can hang the plant light higher and the cover area is larger. In flowering stage you can hang the plant light lower and the cover area is smaller because the plant needs more light at this stage. You have to compare different coverage areas to choose the plant light that suits you.

PH-B-L2,Led Grow Light Cob,1000W Cob Grow Light Indoor,1000W Led Grow Light,320W Cob Grow Light
Shenzhen Phlizon Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.szledplantgrowlights.com