Fertilizer refers to fertilizer applied to or mixed with seeds when planted or planted. When the fertilizer is applied properly, it can meet the nutrient needs of the crop in time, and save the labor of topdressing; if improperly applied, it will damage the seed. Therefore, pay attention to "five no choices" when applying seed fertilizer:
   First, do not choose a fertilizer with corrosive effects. Ammonium bicarbonate and ammonia water are volatile and corrosive. They are easy to smear seeds and seedlings. Superphosphate contains free sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid, which can cause damage to seed germination and seedling growth. Generally, it is not suitable for seed fertilizer. Such fertilizers should be applied under the seeding ditch or separated from the seed by a certain soil layer, or mixed with superphosphate and soil fertilizer.
   The second is not to choose a fertilizer with toxic effects. Urea contains a small amount of biuret, which is toxic to seeds and seedlings.
   The third is not to choose fertilizers containing harmful ions. Chemical fertilizers such as potassium chloride and ammonium chloride contain chloride ions, which, when applied to the soil, produce water-soluble chlorides, which are detrimental to seed germination and seedling growth. The nitrate ions contained in fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate and potassium nitrate also have an effect on seed germination.
   Fourth, do not choose strong alkaline fertilizer. Strong alkaline fertilizers such as kiln ash potassium fertilizer and steel slag phosphate fertilizer should not be used as seed fertilizer. The kiln ash potassium fertilizer has strong hygroscopicity, and releases a large amount of heat after absorbing water, which easily burns out seeds and radicles. When it is necessary to make a seed fertilizer, it must be mixed with organic fertilizer, applied to the seeding ditch, and then planted with soil.
   The fifth is not to choose unfertilized farmyard manure. In rural areas, manure, manure and urine are commonly used as seed fertilizers. If they are not decomposed, a large amount of heat is released during the fermentation process, and the roots are easily burned, and ammonia is burned to burn the seedlings. Therefore, the unfertilized organic fertilizer should not be applied, and it can be fertilized after being fermented at high temperature and fully decomposed. In production, ammonium sulfate, superphosphate, heavy superphosphate, and decomposed organic fertilizer can be applied as seed fertilizers.
Equilateral Dispersive Prisms,Optical Prisms. ... High Refractive Index; Low Abbe Vd Number for Maximum Dispersion; Material: ZF2, N-SF11, CaF2, or ZnSe,H-K9L
Equilateral prisms are normally used for the dispersion of light into its different colors. Light incident at an oblique angle to the first face is dispersed according to its wavelength and emerges as a spectrum from the opposite face
Equilateral dispersing prisms disperse a light into its different colors and are used for spectrum analyzing experiments and instruments. Each colors in the light incident at an oblique angle to the first face is bent in different angle by the difference of refractive index of the glass according to wavelength and emerges as a spectrum from the opposite face, Dispersive prisms are typically used at the minimum angle of deviation
- The roof angle of 60 degrees causes the best combination of wide dispersion and low reflection losses. A glass with large dispersive power or small Abbe`s number leads to large angular dispersion.
- We offer both BK7 and fused silica for a selection of wavelength range from UV to near IR. We recommend a prism of BK7,if the light is not UV, because the angular dispersion of BK7 is larger than that of fused silica.
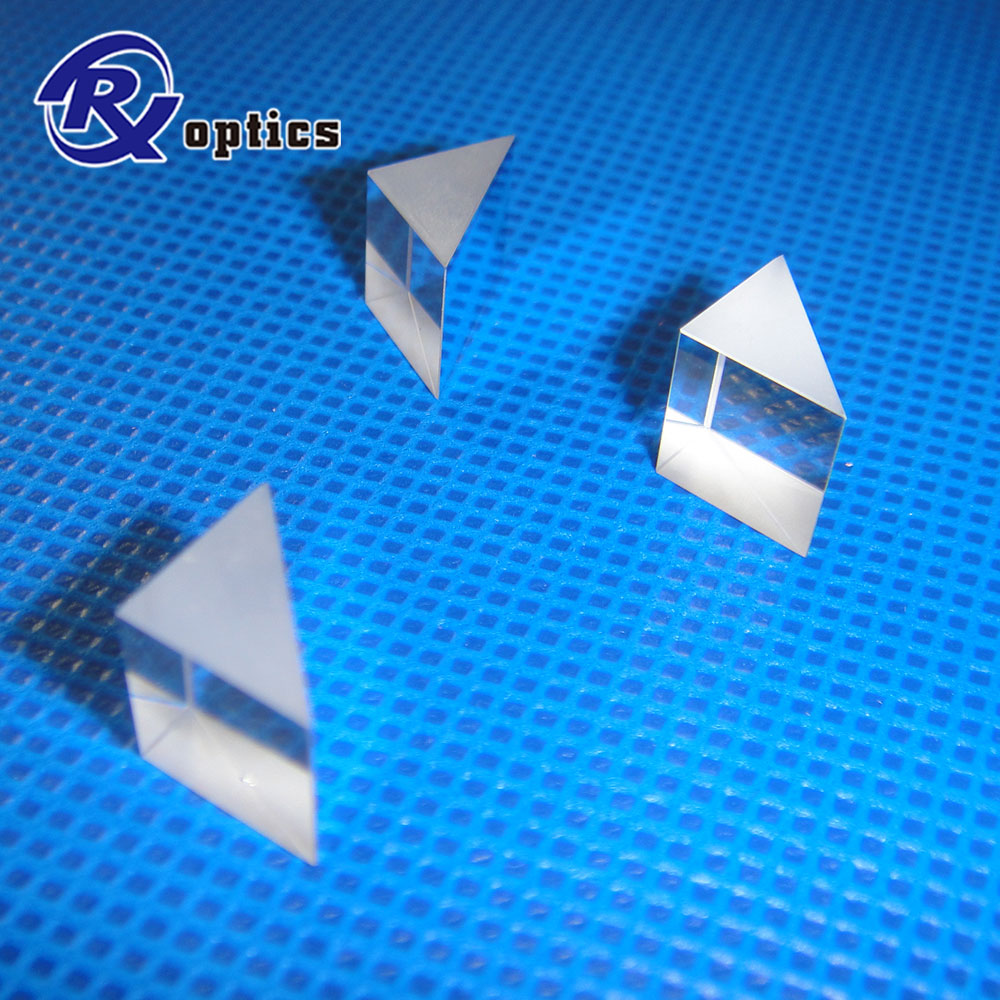
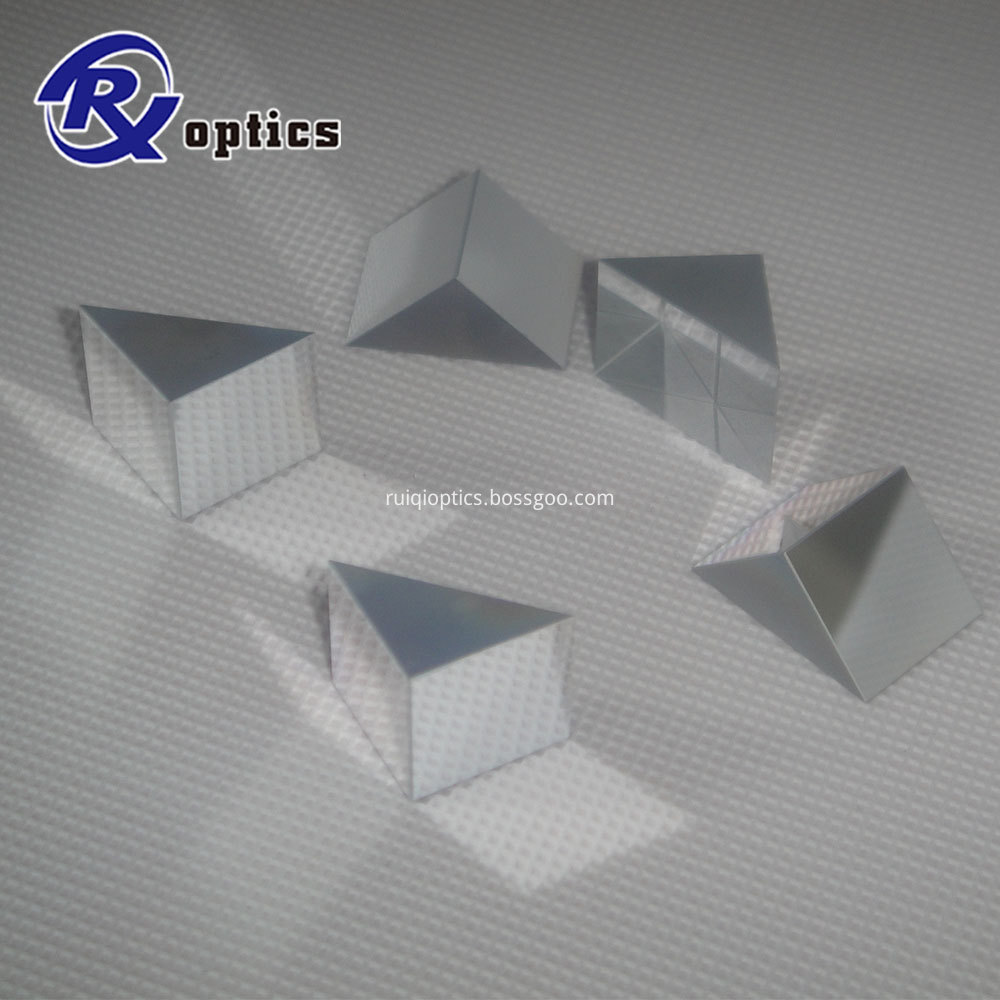
Equilateral Prisms,Equilateral Dispersing Prisms,Equilateral Dispersing Prism,Equilateral Glass Prisms
Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.ruiqi-optics.com