In the smelting process of aluminum alloy, due to the oxidation of aluminum and the interaction of aluminum with the furnace wall and refining agent, the loss of non-recoverable metal is called burning loss. The metal contained in the burnout and slag is collectively referred to as a melt loss. The use of flame reverberatory furnace melting aluminum alloy, due to different charge, the slag amount of 2% to 5% of the charge, and the amount of aluminum in the slag is about 40-60% of the slag amount. Therefore, it is of great significance to properly treat the aluminum slag and recover the aluminum from the slag to reduce the melting loss. The practice of 5t flame reverberatory furnaces for smelting aluminum alloys introduces methods for treating aluminum slags to reduce melt loss.
1 Measures to reduce aluminum slag: During the melting process of aluminum alloy, as the amount of slag increases, the melting loss of aluminum increases, and the amount of slag is related to factors such as the smelting temperature, charge status, and production process. Reduce the amount of slag from the following aspects:
(1) Reasonable furnace geometry and order of addition;
(2) Strictly control the smelting temperature to prevent overheating. The flame spray should have a certain angle so as to melt quickly and shorten the smelting time;
(3) The proper flux and refining time, the stirring should be stable, do not destroy the oxide surface oxide film, timely covering the aluminum melt;
(4) Classifying and cleaning the waste aluminum, and comparing the surface area of ​​the finely divided charge with a press;
(5) Treatment of slag before slagging;
2 slag treatment
(1) Treatment before slag slag: The slag that floats on the surface of the melt after refining is better in wettability with the melt, the wetting angle is less than 90o, and a considerable amount of melt is mixed in the slag. This part of the melt is granular Disperses in the slag and adheres to the slag. When the melt temperature is low, the wettability of the two is better. If the slag is at this time, the weight of the melt discharged with the slag is about 60% of the slag weight. The slagging agent with a slag amount of 1 ‰ to 2 å‡åŒ€ is evenly sprinkled on the surface of the melt to reduce the aluminum content in the slag. The reaction of the slagging agent with the aluminum liquid is as follows: Na2SiF6→2NaF SiF4; 2NaFAl2O3→NaAlO2NaAlOF2; 4NaF2Al2O3→3NaAlO2NaAlF4; 6NaFAl2O3→2AlF3 3Na2O The reactant AlF3 reacts exothermically with aluminum and oxygen, releasing the heat, so that The viscous slag becomes loose powdery dry slag. In this way, the wettability of the aluminum melt and the oxides in the slag is reduced, and the particulate aluminum droplets mixed in the slag are released and returned to the melt.
(2) Aluminum slag treatment after tapping: It should be pointed out that after the above treatment, the slag extracted is still mixed with aluminum droplets. When the slag is dipped, it is first dipped into the iron box with perforations so that a part of the aluminum melt adhering to the slag can leak out. After the slag is finished, pour the slag into the prepared pit (after special treatment), sprinkle some slagging agent into the slag, and stir to mix the slag and slagging agent. After 5 to 10 minutes, remove the residue from the pit. Out. Relying on the rapid warming effect of the slagging agent, the slag temperature reached about 950°C, the oxide film around the aluminum droplets in the slag cracked, and the aluminum droplets gradually fell down to the bottom with their own gravity. After the secondary treatment of the slag contains only a small amount of aluminum particles, the cooled slag is stored in a certain place, from which to pick the aluminum particles. The above method for treating aluminum slag for recycling is simple and feasible. At present, in the melting process of aluminum alloy, the melting loss is reduced to 1.6%, sometimes reaching 1.4%. If 5000 tons of aluminum alloy is produced every year, the original economic loss caused by melting loss can be reduced by 400,000 yuan, and the economic benefit is considerable. A series of improvements, but they are all intermittent operations, small improvements can not significantly reduce the price of titanium. Therefore, a new, low-cost, continuous process should be developed to fundamentally solve the problem of high production costs. For this reason, the researchers conducted a lot of experiments and research. The current research focuses on the following methods: Electrochemical Reduction In order to reduce costs, direct removal of oxygen from metallic titanium has been studied. Electrochemical methods have been used abroad to reduce the concentration of dissolved oxygen in titanium below the detection limit (500 ppm). They believe that in the process of electrochemical deoxygenation, the oxygen-removing agent calcium is produced when the calcium chloride molten salt is electrolyzed, and O2- is precipitated as CO2 or CO at the anode. This new high-purity method is not only used for the deoxidation of titanium, but also for rare earth metals such as lanthanum and cerium, and can reduce the oxygen content to 10 ppm.
The industrialization experiment process of the electrochemical method is as follows: First, the titanium dioxide powder is cast or pressure-formed, and then sintered as a cathode, graphite as an anode, CaCl2 as a molten salt, and electrolysis in graphite or titanium crucible. The applied voltage is 2.8V to 3.2V, which is lower than the decomposition voltage of CaCl2 (3.2V to 3.3V). After a certain period of time after electrolysis, the cathode was changed from white to gray. As observed under the SEM, 0.25 μm of TiO 2 was converted to 12 μm of titanium sponge. Taking calcium chloride as molten salt, the main reason is that its price is low, and O2- has a certain degree of solubility, so that the precipitation of titanium is not easy to be oxidized; In addition, CaCl2 non-toxic, no pollution to the environment.
Compared with TiCl4 molten salt electrolysis, the raw materials used in this method are oxides rather than volatile chlorides, so the preparation process can be simplified, and the product quality is high; the redox reaction between the valence ions of titanium does not occur; the anode is precipitated The gas is pure oxygen (inert anode) or CO, CO2 mixed gas (graphite anode), easy to control, no pollution.
This method not only promotes the reduction reaction near the cathode but also deoxidizes the reduced titanium. This method, which combines the direct electrolytic reduction of oxides with the electrochemical deoxidation method, is a novel method for the preparation of titanium and has become an attractive method in the titanium extraction process. According to data calculated by the British Nature Journal published paper in 2000, with this method, the production cost per ton of sponge titanium is reduced by about 13,000 U.S. dollars. If the current global output of 560,000 tons is changed by this electrochemical method, it will save 770 million yuan annually. Dollar production costs.
Amstrong et al. improved the Hunter method to make it a continuous production process. The procedure is: First, the TiCl4 gas is injected into the excess molten sodium. The excess sodium serves to cool the reduced product and carry the product into the separation process. Remove the sodium and salt to get the product titanium powder. The oxygen content in the product is 0.2% lower, reaching the standard for secondary titanium. Slight improvements to the process can produce VTi, AlTi alloys. Compared with the Hunter method, this method has the advantages of continuous production, low investment, wide range of product applications, and decomposition of byproducts into sodium and chlorine.
This method has approached industrial production, but there are still several problems, such as how to further reduce the oxygen content, how the product cost and so on.
The TiCl4 electrolytic reduction method is superior to the Kroll method and the Hunter method in view of the electrolysis process. Therefore, from Kroll's development of the thermal reduction method, there was an idea to convert the titanium smelting process to electrolysis.
The TiCl4 electrolytic reduction method is the only method that was once thought to be a possible replacement for the Kroll process. The United States, the former Soviet Union, Japan, France, Italy, and China all conducted long-term and in-depth studies on it. The use of the TiCl4 electrolytic reduction method technically requires that TiCl4 be first converted into the lower chloride of the titanium and dissolved in the melt. At the same time, the cathode region and the anode region must be separated and the electrolytic cell must be sealed.
Some people in Italy have been working on the TiCl4 electrolysis method. They analyzed the chlorination electrolysis data and found that when the temperature is above 900°C, there is no Ti2+ or Ti3+, but only Ti4+ and Ti in the electrolyte. Based on this, the established electrolytic process is that TiCl4 gas is injected into the multilayer electrolyte and absorbed. This multiphase layer consists of potassium, calcium, titanium, chlorine, fluorine ions, and potassium, calcium, etc., and separates the titanium cathode and the graphite anode. Liquid titanium generated in the lower layer sinks to the bottom of the bath to a copper crucible with water cooling to form an ingot. However, the purity of titanium obtained by this method is not high and the efficiency is low.
It is expected that titanium, which has superior properties and is rich in resources, has attracted attention as an ideal material since the latter half of the 20th century, but so far it has not emerged from rare metals. The annual production of titanium in the world is only tens of thousands of tons. As the Kroll method is to reduce titanium tetrachloride with metal magnesium to obtain spongy titanium metal, together with the long process, many processes and other factors, resulting in high cost of titanium sponge, affecting the application of titanium in various industries, so that It has not been widely used in many application areas. However, we believe that with the development of science and technology, the development of new production processes for titanium metal, the reduction of production costs, and the expansion of production scale will truly become the century of titanium in the 21st century.
Into the surface of the workpiece, the formation of a strong combination of metallurgical sedimentary layer. The mains power supply discharge cycle is 10-3~10-1 second. High-frequency discharge and high-speed rotation scanning of the electrode rod (electrode) on the workpiece surface can realize large-area and high-efficiency deposition coating.
Why can we achieve "cold welding" (low heat input)?
This is because the discharge time (Pt) is shorter than the discharge interval time (It). During the discharge interval, the heat rapidly spreads to other parts of the workpiece. Therefore, the heat is not concentrated in the processing part of the workpiece, and the real meaning of cold welding is realized.
Why is the combination strength high?
Electrode rods (electrodes) are instantaneously ionized by the arc and transferred to the workpieces that come in contact with them. Simultaneously with the high temperature (8000-10000 °C) of the plasma arc, a solid diffusion layer like a disc is formed under the surface of the workpiece. High strength will not fall off.
Precision mold repair cold welding machine equipment features:
The advanced and reliable equipment, German local technology, and international standard high-power argon protection can work long hours. ¤ Rotary self-destructive electrode, high deposition, surfacing efficiency, metallurgical bonding, coating quality. A multi-purpose machine can be used for surfacing deposition, surface enhancement and other functions. By adjusting the discharge voltage of the device, and the frequency of discharge, the required thickness or smoothness of the surfacing or strengthening coating can be obtained. ¤ Simple operation, low heat input, no need of preheating during mold repair, no heat input during the instant welding process, so the mold does not deform, no annealing, undercut and residual stress, does not change the state of the metal structure of the mold or product. Tantalum electrodes have a wide range of sources and are economical and practical. ¤ Wide range of substrates, including low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, die steel, stainless steel, tool steel, cast iron, cast steel, cast aluminum, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, nickel alloy, carbon tungsten alloy, etc., as well as all conductive Conductor. Environmental protection, no pollution in the work process. ¤ Economical, on-site online repair, increase production efficiency, save time and costs. ¤ The repair accuracy is high. The thickness of the coating ranges from a few micrometers to a few millimeters. It only needs to be polished and polished. Can also be car, milling, planing, grinding and other mechanical processing, and electroplating and other post-processing.
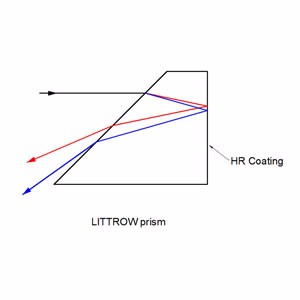
Littrow prisms feature 30°, 60°, and 90° angles .30° - 60° - 90° Littrow Dispersion Prisms can be used for a variety of applications. Uncoated littrow dipersion prisms are used to disperse light into its component spectrum. Coated littrow dipersion prisms are used to deviate the line of sight by 60°.
Dispersion Prisms (Uncoated)
Collimated white light enters into the A-C surface of the prism, is reflected at the hypotenuse surface, and then dispersed into its component spectrum at the B-C surface. Although Littrow prisms produce narrower dispersion than equilateral prisms, Littrow prisms are typically less expensive.
Beam Deviation Prisms (Coated)
Incident light enters into the aluminum coated B-C surface of the prism at the nominal angle and returns back using the same path. In spectrum dispersion applications utilizing white light, the resolution performance of Littrow prisms is equal to equilateral prisms since the optical path length through the glass substrate is the same distance round-trip. Additionally, light entered into the A-C surface will reflect twice inside the glass substrate before being emitted through the hypotenuse surface at 60°.
Dispersion Prism,Optical Dispersion Prisms,Beam Deviation Prisms,Inked Dispersion Prism
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.csoptlens.com